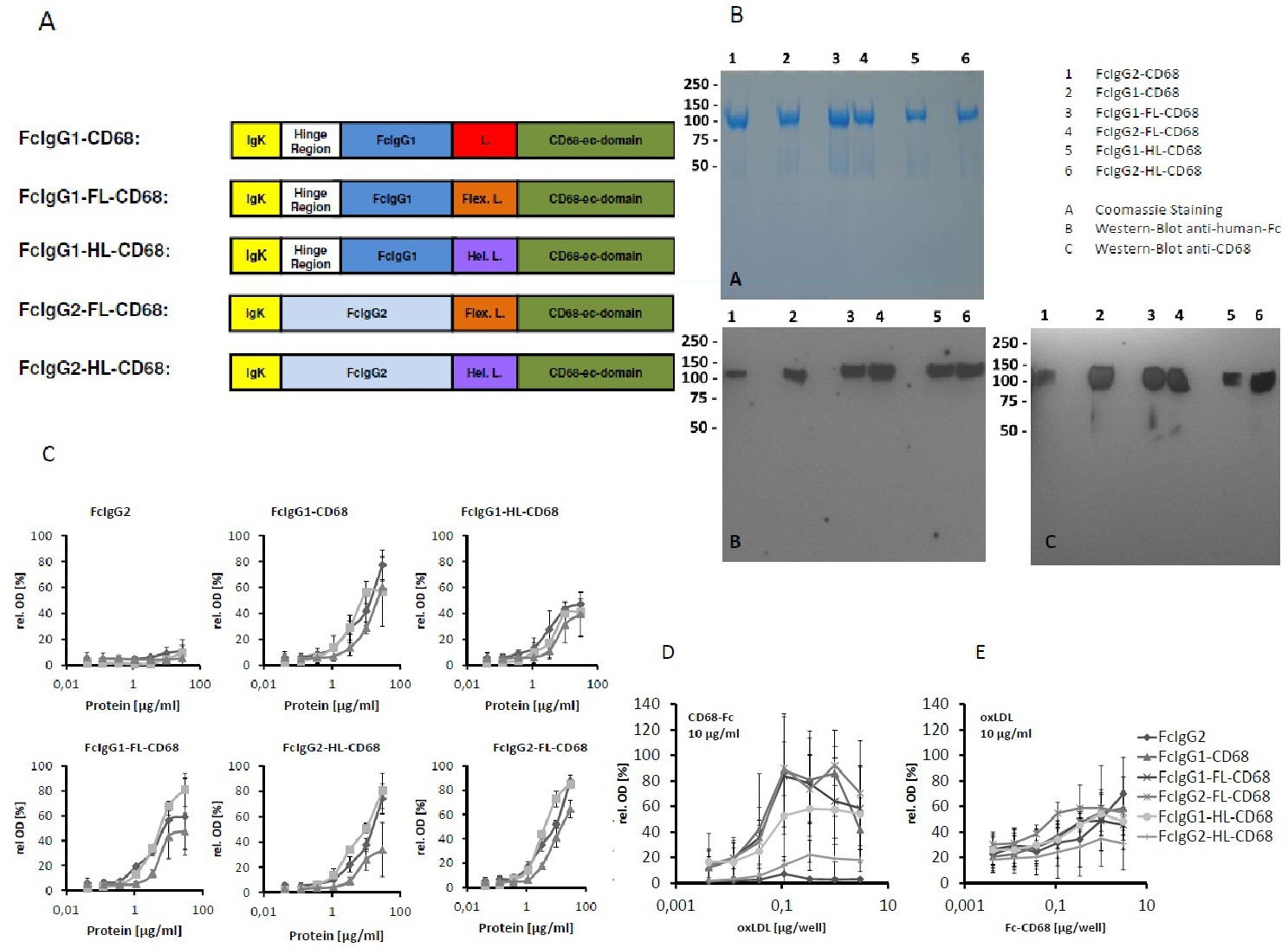
Fig. 1. (A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of Fc-CD68 fusion proteins. IgK: Ig Kappa leader sequence, hinge region, Fragments crystalizable (Fc) from human IgG1 or IgG2 were fused with the extracellular domain of CD68 using different linkers. L: short linker (GGR), Hel. L: linker with supposed rigid, helical conformation, Flex. L: linker with supposed flexible structure. (B) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE and Western-Blot analysis of the purified Fc-CD68 fusion proteins. A 4-20% PAA gradient gel was used for all analysis. A: Coomassie staining. B: Western Blot with an anti human Fc antibody. C: Western-Blot with an anti CD68 antibody. (C) Binding ELISA with lipoproteins oxLDL, HDL and LDL (1 µg/well) immobilized on a 96-well Maxisorp plate. Dilution series of the different Fc-fusion proteins in the soluble phase were tested for binding. The Means ± SEM of 4 independent experiments. (D) Binding ELISA with immobilized oxLDL. A dilution series of oxLDL (0.004-3 µg/well) was immobilized on a 96-well Maxisorp plate and binding of the different Fc-CD68 fusion proteins was tested using a fixed concentration in the soluble phase (10 µg/ml). The Means ± SEM of 4 independent experiments. (E) Binding ELISA with immobilized fusion proteins. A dilution series of the Fc-CD68 fusion proteins (0,004 - 3 µg/well) was immobilized. oxLDL (10 µg/ml) in the soluble phase was tested for binding. The Means ± SEM of 4 independent experiments are shown.